In order to have a healthy and meaningful life, people need to have a unifying purpose behind everything they do. Recognizing the importance of this at a young age (as I saw many lacking one struggle greatly), I decided to devote myself to the pursuit of truth, regardless of where it took me. From this, I quickly realized how difficult this was, as on virtually every issue, there is a massive amount of ambiguity, which inevitably leads you reaching false conclusions produced from your existing biases.
Because of this, whenever I try to figure out why something “bad” is happening, I take numerous possibilities (often over a dozen) into consideration, and frequently never fully commit to any as I don’t feel a definitive case was made for any of them—an approach which lies in stark contrast to those who come across one explanation and immediately commit to espousing it (as it “makes sense”). Rather, I patiently wait and have faith I will eventually uncover the thread that ties all the disparate pieces together (which when finally revealed, is an immense source of joy).
Note: this is why, while I sometimes claim things are true, I am also quite deliberate in prefacing other statements with “I suspect” or “I believe.”
The hepatitis B vaccine for example, is one of the most controversial vaccines on the immunization schedule, as some of the strongest arguments both in favor and against vaccination exist for its current use. I’ve hence spent decades trying to figure out why we give it to every newborn in America, and have heard numerous compelling explanations to account for this, but never found one that appeared to explain everything.
Fortunately, two weeks ago, a reader finally provided the answer to this question—an answer I was obligated to publicize, as tomorrow on Thursday (9-18-2025), the ACIP (the independent advisory committee which decides which vaccines are “recommended” to America), after decades, will at last be seriously re-evaluating the appropriateness of giving it to all newborns.
A recent Highwire clip, in turn, highlights how controversial this subject is, as individuals on both sides have spoken out aggressively in favor of or in opposition to potentially changing the existing hepatitis B recommendation:
Note: at a contentious hearing today, the now dismissed CDC director (Daskalakis’s boss), when repeatedly pressed by Senator Rand Paul to do so, was unable to provide any rationale for why we give every newborn the hepatitis B vaccine, despite widely decrying any attempt to overturn it—again illustrating the shaky ground this policy rests upon.
Hepatitis B Safety Concerns
Since entering the market, the hepatitis B vaccine has been marred with safety concerns, particularly after it was given to every child in America. What follows is a brief summary of some of those concerns:
• As early as 1976, one researcher cautioned that since autoimmunity is involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B infections, it they might also be provoked by molecularly similar hepatitis B vaccines.
• One researcher, Bohn Dunbar (a respected vaccine researcher who was a medical school professor), after her brother and research assistant both developed autoimmune and neurological injuries from the vaccine in 1994, devoted herself to exposing the frequent pattern of autoimmune complications from the vaccine (e.g., “Dr. Dunbar has also been in contact with numerous physicians and research scientists from several countries who have independently described thousands of identical severe reactions occurring in Caucasian recipients of the vaccine”). In turn, due to both her prestige and ability to navigate the academic publishing system, she brought significant attention to this subject (e.g., see this 1999 Washington Post article).
• A 1998 Article in Scientist highlighted growing concerns threatening to derail the hepatitis B vaccine program, such as more and more people claiming it caused serious autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis [RA], optic neuritis, and multiple sclerosis [MS]), that one doctor had collected over 600 cases of this happening, and that in July, attorneys representing 15,000 people sued France’s government for exaggerating the vaccine’s benefits and downplaying its risks.
• Shortly after, France suspended hepatitis B vaccinations in schools (to assess if it could cause demyelinating diseases), which the WHO, the ACIP, and France’s medical associations all strongly condemned due to it weakening public confidence in the vaccine.
• In January 1999 (one of the last times major news networks still aired programs critical of pharmaceutical interests—as Clinton has recently legalized pharmaceutical companies buying them out), ABC news hosted an almost entirely forgotten program on the hepatitis B vaccine, which featured a chief CDC and Merck official (who claimed mass vaccination justified preventing a few hepatitis cases and that no injuries attributed to the vaccine were actually caused by it) along with many vaccine injured patients, including both injured adults and parents of severely injured children.
Shortly after, at a May 1999 Congressional hearing discussing the merits of universal hepatitis B vaccination of newborns, in addition to many espousing the need for it, the following objections were raised in testimonials from experts and vaccine-injured parties who testified against the practice:
Severe Adverse Reactions: Numerous serious side effects were discussed, including infant death, seizures, autism, dysautonomia, MS, RA diabetes, and rare cases of liver cancer in children post-vaccination (along with established mechanisms for the autoimmune responses). VAERS data in turn, indicated over 8,000 reactions, including 43 deaths in children under 2 in 1997. In contrast, there were only 95 annual hepatitis B cases in this demographic (with comparable, or smaller, numbers seen in other datasets)—suggesting injuries vastly outweighed prevented hepatitis cases (particularly since less than 1% of injuries are typically reported to VAERS and infant deaths from hepatitis were virtually non-existent in the pre-vaccination era).
Note: at each point in time where the safety of the hepatitis B vaccine was questioned, the same pattern of injuries (e.g., characteristic autoimmune disorders and infant deaths) in VAERS was cited, with the total number of them continually increasing as the years went by.
Inadequate Safety Monitoring and Research: Adverse reaction reports were often ignored or dismissed, with short trial durations (4–5 days), missing delayed reactions like MS or diabetes, which may appear years later. No studies focused on newborns or genetic predispositions, and underreporting was common due to physician denial.
Lack of Informed Consent and Coercion: Parents received inadequate risk information, with CDC materials omitting serious adverse effects listed in manufacturer inserts. Newborns were vaccinated without parental consent, and some faced coercion, including threats of social services intervention.
Questionable Mandate: Vaccinating low-risk newborns for an adult-associated disease is inappropriate, particularly since immunity can wane before adolescence and 10–30% of individuals fail to produce antibodies, questioning efficacy.
Conflicts of Interest: Pharmaceutical influence on health agencies raised doubts about study objectivity.
Vaccine Injury Compensation Issues: The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program denied most claims, leaving victims unsupported despite a $1 billion trust fund, with restrictions limiting filings for hepatitis B vaccine injuries.
Note: most of the above has also been said about many other vaccines over the decades. Likewise, in a 1999 testimony before the Ohio legislature, another physician noted that most of the deaths following hepatitis B were classified as SIDS (a condition extensive evidence shows is strongly linked to vaccination) yet SIDS was almost always defined as occurring between 1 month to 1 year of age, and that prior to the hepatitis B vaccine being given to newborns, it rarely if ever affected children under 2 months of age—however in VAERS, many cases labeled as SIDS were reported in infants under one month of age following the vaccination.
One of the Congressional witnesses, in turn, produced an excellent (referenced) summary of the major issues with the hepatitis B vaccine which included two cases he’d observed it causing encephalomyelitis (resulting in a two week coma for one, a four week coma for the other, along with optic neuritis and significant neurological disability for both, and no clear conventional explanation for what had occurred) along with many cases of it causing chronic fatigue syndrome. He then compiled a list of dozens of studies demonstrating that the hepatitis B vaccine was linked to a myriad of autoimmune disorders, as did another author 15 years later (in a 2015 textbook on the subject). Those studies (which are likely only the tip of the iceberg) are as follows:
Multiple Sclerosis,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 myelitis,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 optic neuritis,1,2 Guillain–Barré syndrome,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 neuropathy,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 myopathy,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 Myasthenia Gravis1,2
Arthritis,1,2,3,4 Lupus,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18 juvenile dermatomyositis,1,2,3 Still’s disease1
Vasculitis (general,1,2,3 pulmonary and cutaneous,1,2 Churg-Strauss,1,2 Henoch–Schonlein purpura,1 Kawasaki’s disease1), thrombocytopenia,1,2,3,4,5,6 antiphospholipid syndrome1,2
Lichen planus,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18 bullous pemphigoid,1,2 erythema multiforme,1,2,3 Gianotti–Crosti syndrome,1,2 alopecia,1
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome,1,2,3,4 Graves’ disease,1,2 glomerulonephritis1
As mentioned above, since the start, it was widely believed that the autoimmune conditions the hepatitis B vaccine caused were due to its antigen having a significant overlap with human myelin (particularly since many of the autoimmune disorders associated with the vaccine were also observed to sometimes occur from a hepatitis B infection).
The molecular mimicry of the vaccine, in turn, was a hotly debated topic that all medical authorities denied was occurring. As it was not possible to assess with the technology of the time, the absence of evidence for it was treated as evidence that it did not.
Note: a definitive 1994 report by the Institute of Medicine noted that while preliminary data existed for many of the injuries attributed to the hepatitis B vaccine, no further research had ever been done, so there was insufficient evidence to prove or disprove a link between these conditions, and concluded its report on the safety of the childhood vaccines by declaring that the lack of adequate data regarding many of the adverse events under study was of significant concern to the committee (but as you might guess, the studies they requested still have not been done).
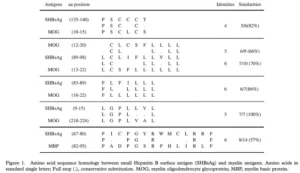
However, while it was not possible to assess then, a 2005 study showed the hepatitis B vaccine did, indeed, have a significant overlap with myelin and more importantly, that 60% of its recipients also developed immune reactivity to the myelin coasting their nerves (which in the majority of cases persisted for over 6 months). Sadly, by the time this was discovered, the use of the hepatitis B vaccine had been normalized, and public debate on its safety or autoimmunity risk had long since ended.
Likewise:
• A 2005 VAERS study comparing adults who’d received a tetanus-containing vaccine to a hepatitis B vaccine found they were much more likely to develop a variety of autoimmune disorders (5.2X for MS, 18X for RA, 14X for optic neuritis, 9.1X for lupus, 7.2X for alopecia, 2.6X for vasculitis, and 2.3X for thrombocytopenia). A similar 2002 study found a 6.1X increase for chronic arthritis (persisting for at least one year), which affected women 3.5X as much as men, and on average occurred 16 days after vaccination.
• A 2015 study found cases of MS in France rose by 65% in the years following an aggressive national campaign to increase hepatitis B vaccination rates, and that a statistically significant correlation existed between the number of hepatitis B vaccine doses given and the number of MS cases 1-2 years later.
• A 2004 study analyzed primary care records from across England to compare 163 MS patients with 1,604 randomly selected matched controls without MS. It found that MS patients were three times more likely to have received the hepatitis B vaccine within three years of symptom onset, with no similar risk linked to tetanus or influenza vaccines—indicating this was a specific issue with the hepatitis B vaccine.
• A 2009 study in children found that the GSK’s hepatitis B vaccine, which contains five times more yeast protein antigen than other brands, was associated with a 2.77X increased risk of developing MS in vaccine-compliant children. A smaller increase (1.5X) was observed for other CNS inflammatory demyelinating disorders in children who adhered to recommended vaccination schedules.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine has also been repeatedly linked to autism and other developmental disabilities:
• In a June interview with Tucker Carlson, Secretary Kennedy revealed that in 1999, the CDC conducted a study which found that receiving a hepatitis B vaccine in the first 30 days of life caused a 12.35X increase in autism. As this was unacceptable, they conducted numerous attempts to adjust the data to hide the risk, but were unable to make the link go away, gave up, and never published it.
An abstract of a 1999 study (which is likely what RFK was referring to) was subsequently made available to a Florida Congressmen who had worked with vaccine whistleblowers, which showed (via the CDC’s private VSD database) that when infants received the highest doses of mercury containing vaccines (compared to those who had not been vaccinated), there was a 1.8X increase in neurologic development disorders, a 7.6X increase in autism, a 5.0X increase in nonorganic sleep disorders and a 2.1X increase in nonorganic sleep disorders.
• A 2007 study of 1824 children found boys who received the hepatitis B vaccine (prior to 2000 when it still used thimerosal) were 9 times as likely to have a developmental disability.
• A follow-up 2010 study found neonatal hepatitis B vaccination (compared to no hepatitis B vaccination or simply getting it later in life) made children 3 times as likely to develop autism.
In contrast, the licensing studies for the vaccines only monitored for side effects during a short window long before these side effects would emerge (typically 4-5 days), did not use actual placebos (e.g., the original trials used either aluminum or aluminum and albumin1,2,3 while the later ones compared the vaccine to other “safe” vaccines).
The package insert of Merck’s vaccine noted that in the first 5 days, 17% of adults reported injection site reactions (e.g., pain, soreness, bruising, nodule formation), while 15% of adults and 10.4% of children reported systemic adverse reactions (e.g., fatigue/weakness, headache, fevers above 100°F, malaise, nausea, diarrhea, pharyngitis, upper respiratory infection).
The package of GSK’s vaccine noted after 4 days, 22% of recipients had injection site soreness, 14% had fatigue, and between 1-10% reported dizziness, headaches, and either redness, induration, or swelling at the injection site. Additionally, a variety of more severe conditions were reported in <1% of injections (e.g., anorexia, somnolence, hypotension, a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions, hives, irritability, and weakness). Finally, in adults with diabetes, 3.8% had serious systemic side effects (compared to 1.6% of controls).
Note: non-autoimmune complications have also been attributed to the vaccine (e.g., VAERS revealed a seizure link estimated to affect 1 in 1300 recipients).
In short, despite the fact that most of the research that should have been done never was, it is fair to say the risk profile of this vaccine suggests significant benefit must be seen from it to justify it being given to every newborn infant.
The post Why Is Every Newborn Forced To Get the Dangerous Hepatitis B Vaccine? appeared first on LewRockwell.
0 comments on “Why Is Every Newborn Forced To Get the Dangerous Hepatitis B Vaccine?” Add yours →